Printable Nj 1040Nr Form
The NJ-1040NR form is the New Jersey Nonresident Income Tax Return, designed for individuals who earned income in New Jersey but reside elsewhere. This form must be completed for the tax year from January 1 to December 31, 2021. Ensure all necessary information is accurately filled out to facilitate a smooth filing process.
To get started on your NJ-1040NR form, click the button below.
Open Editor Here
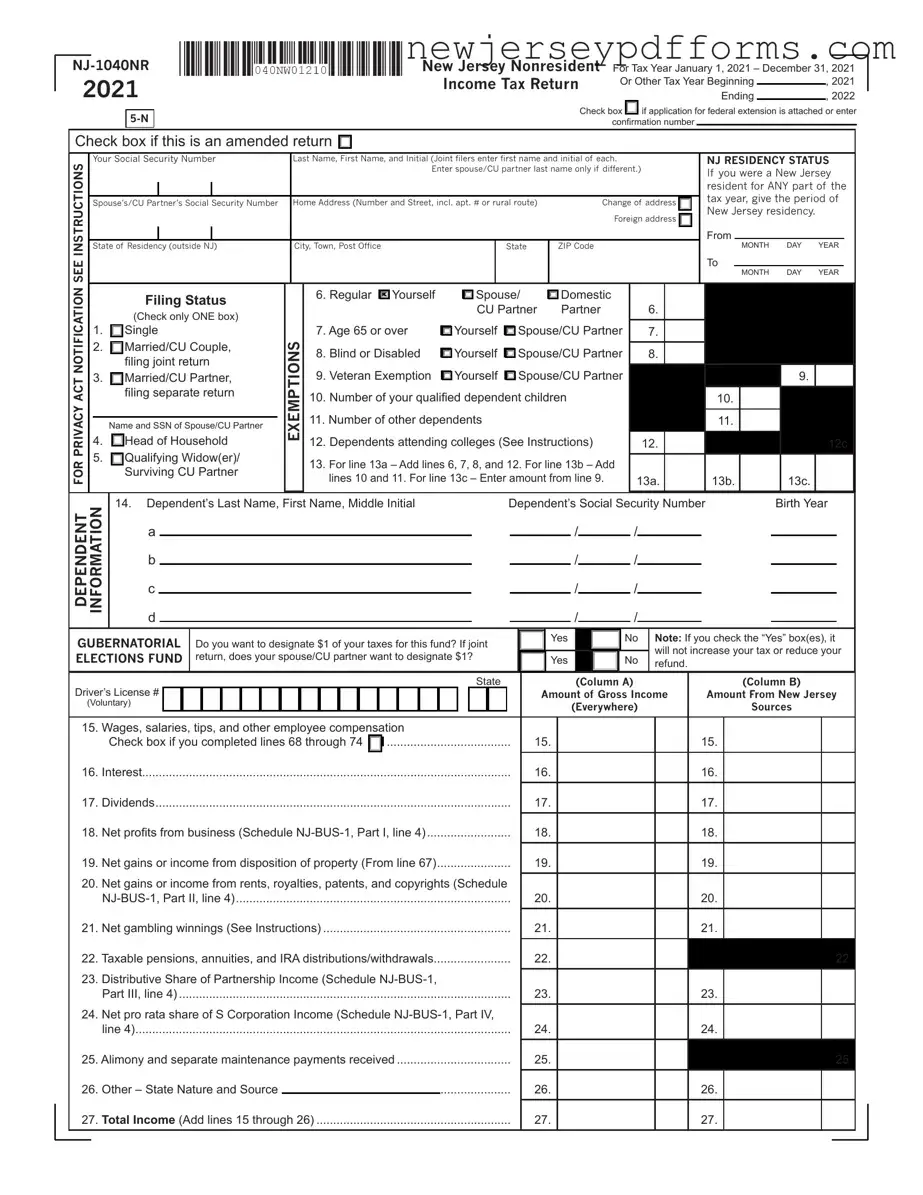
Printable Nj 1040Nr Form
Open Editor Here

Open Editor Here
or
Download Nj 1040Nr PDF Form
Complete the form before time runs out
Edit your Nj 1040Nr online and complete it quickly.