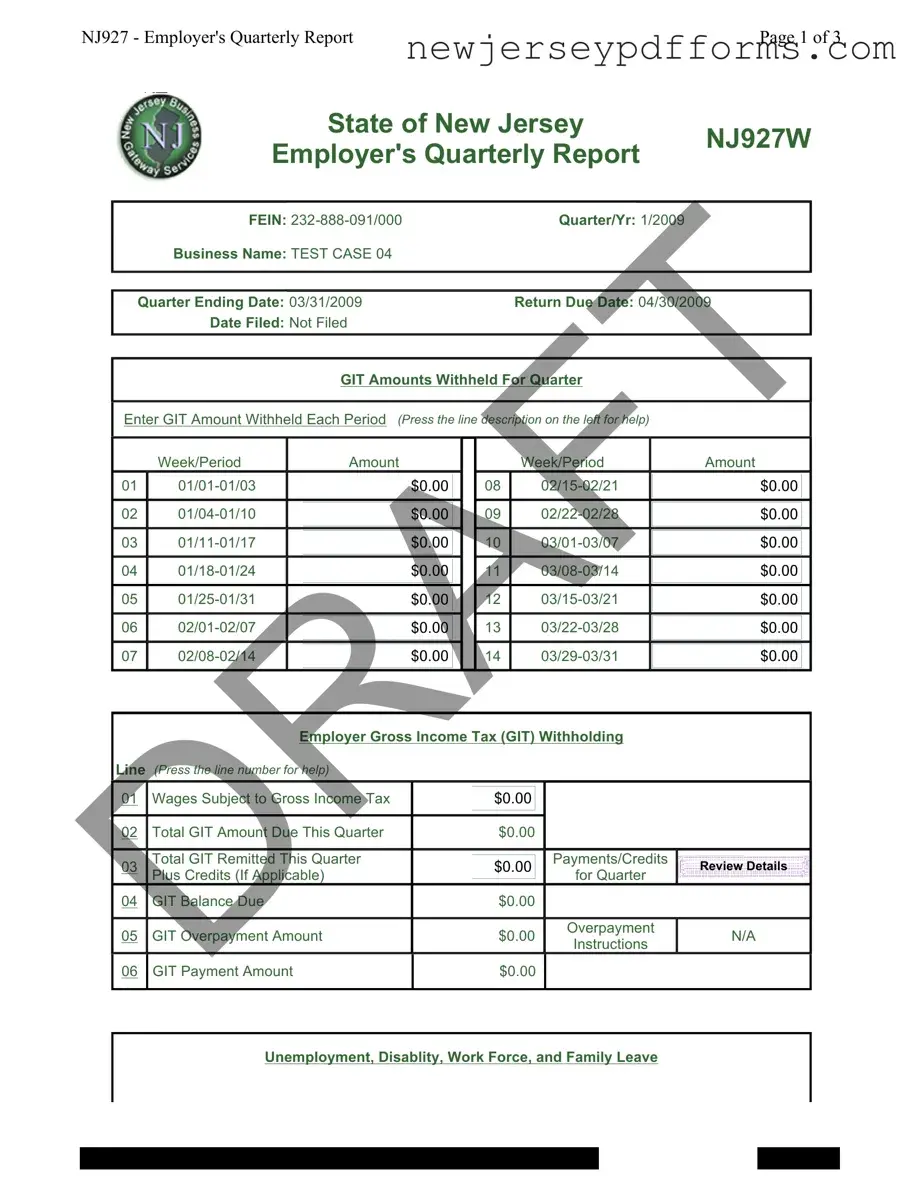
What is the NJ 927 W form?
The NJ 927 W form, also known as the Employer's Quarterly Report, is a document that employers in New Jersey must file to report wages paid to employees and the associated taxes withheld. This form is crucial for ensuring compliance with state tax laws, including the Gross Income Tax (GIT) and other contributions related to unemployment and disability insurance. It provides a summary of the employer's payroll activities for a specific quarter.
When is the NJ 927 W form due?
The NJ 927 W form is due on the last day of the month following the end of the quarter. For example, if the quarter ends on March 31, the form must be filed by April 30. Timely submission is essential to avoid penalties and interest on any unpaid taxes.
How do I complete the NJ 927 W form?
To complete the NJ 927 W form, employers must provide information about the wages paid during the quarter, the number of employees, and the taxes withheld. Each line of the form corresponds to specific data that needs to be filled out. Employers should ensure accuracy by double-checking figures and ensuring that all required sections are completed. Guidance is often available on the form itself, providing assistance for each line item.
What happens if I do not file the NJ 927 W form on time?
If the NJ 927 W form is not filed by the due date, employers may face penalties and interest on any outstanding tax amounts. The state may also take enforcement actions, which could include withholding future tax refunds or taking legal action to recover unpaid taxes. It is always best to file on time or to contact the state for assistance if there are difficulties in meeting the deadline.
Can I amend my NJ 927 W form after it has been filed?
Yes, if an employer discovers an error after filing the NJ 927 W form, it is possible to amend the form. This can typically be done by submitting a corrected form to the state, along with an explanation of the changes. It is important to address any discrepancies as soon as possible to avoid potential penalties or issues with tax compliance.
Where can I find assistance with the NJ 927 W form?
Assistance with the NJ 927 W form can be found through the New Jersey Division of Taxation's website. They provide resources, including guides and contact information for customer service. Additionally, employers may seek help from tax professionals who are familiar with state tax regulations to ensure accurate completion and compliance.